by Andrew Kell | Dec 27, 2022 | Electric Vehicles, Electrification, Energy Storage, Health, Netzero Wisconsin, Renewables, Solar, Wind
This past year, a Project Team consisting of RENEW Wisconsin, Clean Wisconsin, and GridLab commissioned Evolved Energy Research and Cambridge Econometrics to provide modeling, analysis, and reporting for a Wisconsin Zero Carbon Study. The recently released Summary Report provides an excellent overview of the Study results and policy recommendations. This RENEW blog provides additional context and insight into the next steps.
The Technical Report, titled Achieving 100% Clean Energy in Wisconsin, was completed this past summer and provides a first-of-its-kind, economy-wide modeling approach to envision a Wisconsin transition to a zero-carbon future by 2050. The modeling included 1) a baseline scenario as a comparison reference, 2) a 100% Clean Electricity scenario, 3) a Net Zero Economy-wide scenario (also referred to as NZEW), and four additional sub-scenarios that envisioned the NZEW scenario with policy and economic constraints. With NZEW by 2050 as a base assumption, these sub-scenarios further explored scenarios including a) No Transmission Expansion, b) Accelerated Clean Electricity, c) Delayed Action (of electric vehicle and building electrification), and d) Limited Coal and Gas.
The modeling results show a viable zero-carbon future by 2050, but it is a future that requires collaborative planning, supporting policies, and economy-wide investments.
A Grid Evolution
Wisconsin’s current resource portfolio relies heavily on fossil fuel-generating capacity. The figure below, which provides the baseline 2022 capacity assumptions from the model, shows that about 70% of Wisconsin’s current generating capacity relies on coal or fossil gas as fuel sources.
The following pie chart is listed in Gigawatts (GW).
In order to achieve a carbon-free future, clearly existing fossil fuel-generating capacity needs to be replaced with clean energy resources. However, when contemplating the decarbonization of all sectors of the economy, there also needs to be an expansion of generating capacity to serve Wisconsin’s electricity needs by 2050 – a lot more clean energy capacity.
Modeling of the NZEW scenario estimates that when Wisconsin decarbonizes the transportation, building, and other sectors, electricity use will increase by over 160% by 2050, well over doubling Wisconsin’s demand for electricity. Electrification of these sectors is often referred to as ‘beneficial electrification’ as the transition implies moving away from fossil fuels to decarbonized electricity as a fuel source.
To be truly beneficial, the timing of electric vehicle (EV) charging will be essential for load balancing and efficient use of utility infrastructure. This way, while overall electricity usage goes up dramatically, price signals, automatic controls, and utility programs will all allow EVs to charge optimally throughout the year. Currently, it is most economical to charge EVs at night when prices are low. In the future, it may also make sense to send signals to charge during peak solar production during the summer noontime.
The figure below illustrates the capacity expansion needed on the supply side to meet electricity demand growth.
As a result of decarbonization of the grid and beneficial electrification, Wisconsin's demand for electricity in 2050 would be supplied by an estimated 31 Gigawatts (GW) of solar, 21 GW of wind, 7 GW of storage, 7 GW of clean gas, 2 GW hydrogen electrolyzer capacity, and 3 GW of dual fuel electric industrial boilers located in Wisconsin. Of the 31 GW of solar, the model assumed about 2.5 GW would come from rooftop solar based on information from a solar rooftop potential study. Utilities would need to import additional clean energy capacity from outside Wisconsin. The model estimated that imported clean energy would come from about 9.3 GW of solar and 6.3 GW of wind from out-of-state resources.
The figure below provides a snapshot of the clean generation portfolio serving Wisconsin by 2050 under the Net Zero Economy-wide modeling results.
The following pie chart is listed in Gigawatts (GW).
Utility-scale clean energy resources at this scale also require the expansion of transmission investments. For each of Wisconsin’s interties with Minnesota, Iowa, and Illinois, the model estimates that 6 GW of transmission interties are needed for each of these three state interties. This equates to 18 GW of new transmission interties, which is about 3-to-4 times the amount of current Wisconsin transmission interties.
While gas capacity remains in all scenarios, gas serves as a reliability resource operating at just a 5% capacity factor and burning entirely clean, carbon-neutral fuels. In the ‘Limited Coal and Gas’ scenario, existing and less efficient gas units must remain online much longer and operate at much higher capacity factors because new, more efficient gas units are not allowed in this scenario.
In the ‘No Transmission Expansion’ scenario, in-state clean energy resources would have to expand by about 36% above the Net Zero Economy-wide scenario. In this scenario, all new generation capacity must be developed in Wisconsin, as higher capacity factor resources in other states cannot serve Wisconsin’s electricity needs. This scenario would also necessitate the expansion of ‘intrastate transmission’ within the borders of Wisconsin and add $1 billion in costs above the NZEW scenario.
Taking Emissions Down to Zero
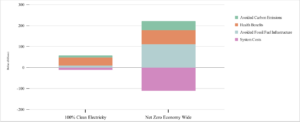
In relation to a baseline scenario, the 100% Clean Electricity scenario will reduce total economy-wide carbon emissions by 24% by 2050. In this scenario, while the grid becomes carbon-free, transportation, building, and other sectors realize only modest decarbonization and still rely on fossil fuels to power cars, homes, and some industrial processes.
It is important to note that concentrating on the decarbonization of the electric grid by 2050 alone only gets Wisconsin to about a quarter of all reductions needed for a carbon-free future across all sectors of the economy. Additionally, in the Net Zero scenario, carbon sequestration and bunkering measures are needed to reduce emissions that come from marginal fossil gas resources. By 2050, a small segment of industries will still emit carbon, either because it is too costly to do otherwise or not technically feasible to eliminate completely. To achieve the target of zero emissions by 2050, the model chooses to rely on carbon sequestration, in which carbon is captured before being released into the atmosphere and then piped via pipeline to appropriate geologic sequestration areas in the country, safely sequestering the carbon.
A Real Benefits Plan
Following the Technical Report, Cambridge Econometrics released a report on The Economic Impacts of Decarbonization in Wisconsin. In combination with health outcomes modeled by Evolved Energy Resources, benefits of the Net Zero Economy-wide scenario include:
- $2 to $4.4 billion in avoided healthcare costs in 2050,
- 28 to 63 fewer deaths per million people from air pollution by 2050,
- 3% growth in Wisconsin’s Gross State Product by 2050, adding around $16 billion to Wisconsin’s economy,
- 68,000 additional Wisconsin jobs, and
- Lower energy costs for Wisconsin’s residents.
The benefits of a zero-carbon future outweigh the costs of the transition per the modeling results. Focusing on energy costs alone, economy-wide investments in renewable resources, heat pumps, EVs, etc., increase by about $111.1 billion in present value. However, the benefits of avoiding fossil fuel costs are about $110.6 billion in present value. When you add the health and economic growth benefits listed above, the net-zero investment makes sense from a business case perspective.
Jenna Greene, RENEW’s Energy Policy Fellow, is currently performing a cost-benefit analysis of the modeled scenarios using the Technical Report and Economic Impacts Report results. When cost-benefit results are available, this blog will be updated.
How We Get There
The transition to a zero-carbon future won’t be easy, as infrastructure build-out, technological innovation, and market development will be needed over the next few decades. As a result, we will need to form public-private partnerships, enact and implement policies, and design cross-sector planning processes that support this transition to ensure it is cost-effective. For quick reference, below is a set of key recommendations from a figure on page 19 of the Summary Report. A complete list of policy actions is provided at the conclusion of the Summary Report.
The release of our Zero Carbon Study is just the start of a dialog on how Wisconsin can reach zero carbon emissions by 2050. The Project Team is further collaborating with partners, businesses, legislators, and state and local government officials on the next steps. For further information, please contact Andrew Kell, Policy Analyst at RENEW Wisconsin, at andrew@renewwisconsin.org.

by Sam Dunaiski | Aug 31, 2022 | Advocacy, Biogas, Electrification, Energy Storage, Geothermal, Hydroelectric, Renewables, Solar, Wind
The world of clean energy received a monumental win earlier this month with the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) will be the backbone of the United States’ effort to decarbonize our energy sector, spur clean energy implementation across all demographics, and significantly grow the clean energy economy.
Here is a breakdown of the bill’s elements:
Renewable Energy Generation
Investment Tax Credits
- Residential Solar: 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC) on project costs until the end of 2032, with a step-down of 26% in 2033 and 22% in 2034. Credits are retroactive for residential installations from 1/1/2022, meaning that homeowners who installed a solar array at any point in 2022 will qualify for the 30% ITC.
- Commercial Solar: 30% ITC on project costs until the end of 2024 (ITC on commercial solar is also retroactive to 1/1/2022). Beginning in 2025, the ITC will be replaced by technology-neutral credits, with the following rules in place:
- 6% base credit; bonus credits up to 30% of costs if the project meets union labor, prevailing wage, and apprenticeship requirements. These requirements do not apply to projects less than 1 megawatt (MW) in size.
- 10% bonus credits if the project meets domestic content requirements.
- 10% bonus credits if the project is sited in an “energy community” – a brownfield site or a community with a recent coal plant closure.
- 10% bonus credits if the project is sited in a low-income community. This only applies to projects that are 5 MW and less.
- 20% bonus credits if the project qualifies as directly serving a low-income residential facility or another economic benefit system.
- Interconnection costs -for projects less than 5 MW- with the utility can be included in the credits.
Production Tax Credits
While the Investment Tax Credit applies to the upfront purchase of parts, materials, and labor, the Production Tax Credit (PTC) functions differently. This credit is a direct payment and applies to the production or output of the generation source. This generation source can be solar, wind, geothermal, biomass, and hydropower, to name a few. These credits are also retroactive from 1/1/2022.
Here is how the PTC breaks down:
- Direct pay value: $0.026 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) starting in 2022; rate rises with inflation.
- Bonus credit of 1.5 cents/kWh if union labor, prevailing wage, and apprenticeship requirements are met.
- 10% bonus credits if domestic content requirements are met.
- 10% bonus credits if the project is sited in an “energy community” – a brownfield site or a community with a recent coal plant closure.
- The PTC is available for nonprofits, state and local governments, rural electric cooperatives, tribal governments, and/or other tax-exempt entities. These organizations previously did not qualify for the ITC.
- PTC will also apply to utility-scale projects.
- Credits are available for ten years after the project is placed into service.
- Direct pay/PTC is not available for residential solar installations.
- PTC is transferable after 2022; however not for individual taxpayers.
- Commercial solar projects can choose either the ITC or the PTC.
Electric Vehicles
New EVs: (Effective 8/16/2022)
- $7,500 tax credit to be divided into two separate credits:
- $3,750 credit for electric vehicles with batteries produced in North America.
- $3,750 credit for electric vehicles using a certain percentage of critical battery minerals extracted or processed in the U.S.
- Vehicles meeting only one requirement will only be eligible for a $3,750 credit.
- Vehicles must cost less than:
- Vans < $80,000
- Pickups and SUVs < $80,000
- Cars < $55,000
- Income requirements:
- Joint tax return < $300,000
- Head of household < $225,000
- Single-payer < $150,000
- Credit will eliminate the limit of 200,000 vehicles per manufacturer.
Commercial Clean Vehicles: (Effective 01/01/23)
- Up to $40,000 tax credit for commercial electric vehicles.
Used EVs: (Effective 01/01/2023)
- $4,000 tax credit or 30% of the vehicle’s sale price.
- The vehicle’s model year must be at least two years older than the current “new” model year.
- Vehicle cost must be less than $25,000.
- Income requirements:
- Joint tax return <$150,000
- Head of household <$112,300
- Single-payer <$75,000
- Used EV tax credits will continue until the end of 2032.
EV-Charging:
- Credits for EV-charging equipment and infrastructure will increase up to $100,000.
- Equipment must be located in a qualified census tract, with similar bonus credits if prevailing wage and apprenticeship requirements are met.
- A direct pay or PTC option is available for charging with transferrable credits.
- Credits will be available until 2032.
Battery Storage
Effective as of 1/1/2023
- 30% ITC for the cost of installation; credits last until 2033. To qualify, batteries must be larger than 3kWh for residential installations and larger than 5kWh for commercial installations.
- Commercial battery credits have similar sliding scales as other ITC items: baseline of 6% with increasing credits for prevailing wage, labor, location, etc.
- Battery storage systems will no longer need to be coupled with solar generation systems to qualify for tax credits.
Energy Efficiency and Electrification
Effective as of 1/1/2023
Federal Tax Credit
- Heat Pumps: 30% of costs, up to $2,000
- Electric Upgrades: 50% of costs, up to $1,200/year
Upfront Discounts
- Incentive levels and eligibility are determined by income
- Heat Pumps: rebates for up to $8,000
- Electric Upgrades: up to $4,000 for breaker boxes/electric service; $2,500 for wiring, and $1,600 for insulation/venting/sealing
Manufacturing and Production
Effective as of 1/1/2023
- $30 billion in PTC to manufacture solar panels, trackers, inverters, wind turbines, batteries, and other critical minerals.
- Solar PV cells – $0.04/watt
- Solar-grade polysilicon – $3/kg
- Solar modules – $0.07/watt
- Wind components – 10% of the sales price
- Battery cells – $35/kWh
- Critical minerals – 10% of the cost of production
- $10 billion in ITC funding for building new facilities to manufacture clean energy products; $4 billion of these funds must be allocated to “energy communities.”
- $500M for manufacturing heat pumps and processing of critical minerals necessary for heat pump production.
Other Items
- Carbon Sequestration Credits (ITC or PTC) for facilities that begin construction before 2033 and provide direct air capture of carbon dioxide. Credits will be issued by a metric ton of carbon capture.
- Clean Hydrogen – credits for production -by unit- of green and blue hydrogen that can be used to offset traditionally carbon-based fuels.
- Sustainable Aviation Fuel – credits for SAF produced by unit (gallon) with increasing credits based on a percentage of greenhouse gas reduction.
- Biodiesel/Alternative Fuels – production credits for fuels produced based on life-cycle emission levels.
- Methane Fees – fees imposed by EPA for facilities that emit more than 25,000 metric tons of CO2 annually.
Additional Provisions
- $500 million for the Defense Production Act, some of which could be used for solar manufacturing.
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund totaling $29 billion overseen by the Environmental Protection Agency.
- Climate Pollution Reduction Grants to state and local governments totaling $5 billion.
- Environmental and Climate Justice Block Grants: $3 billion for disadvantaged communities.
- $2 billion in loan authority for new transmission construction in designated national interest corridors.
- $760 million for the Department of Energy to issue grants to state, local or tribal entities to facilitate siting of high-voltage interstate transmission.
- Additional $1 billion for rural renewable energy electrification loans and expansion of the program to include storage.
- Additional $1 billion for Rural Energy for America Program (REAP), with total grants limited to 50% of the total cost of an eligible project.
- $9.6 billion for loans and financing for rural co-ops to purchase renewable energy, generation, zero-emission systems, and related transmission, limited to 25% of total cost.
- Incentives for build-out of electric vehicle charging networks.
- Extension, expansion, and changes to electric vehicle tax credits, including a new credit for purchasing used EVs.
Conclusion
Much of the implementation and administration of the Inflation Reduction Act is still not understood. This document is meant to summarize the items in the bill that RENEW Wisconsin considers particularly important to the clean energy transition in our state.
For additional information, please utilize the following resources:
Please contact Sam Dunaiski (sam@renewwisconsin.org) with questions.

by Jodi Jean Amble | Jun 1, 2022 | Clean Energy Works, Hydroelectric, Jobs, Renewables, Solar, Wind
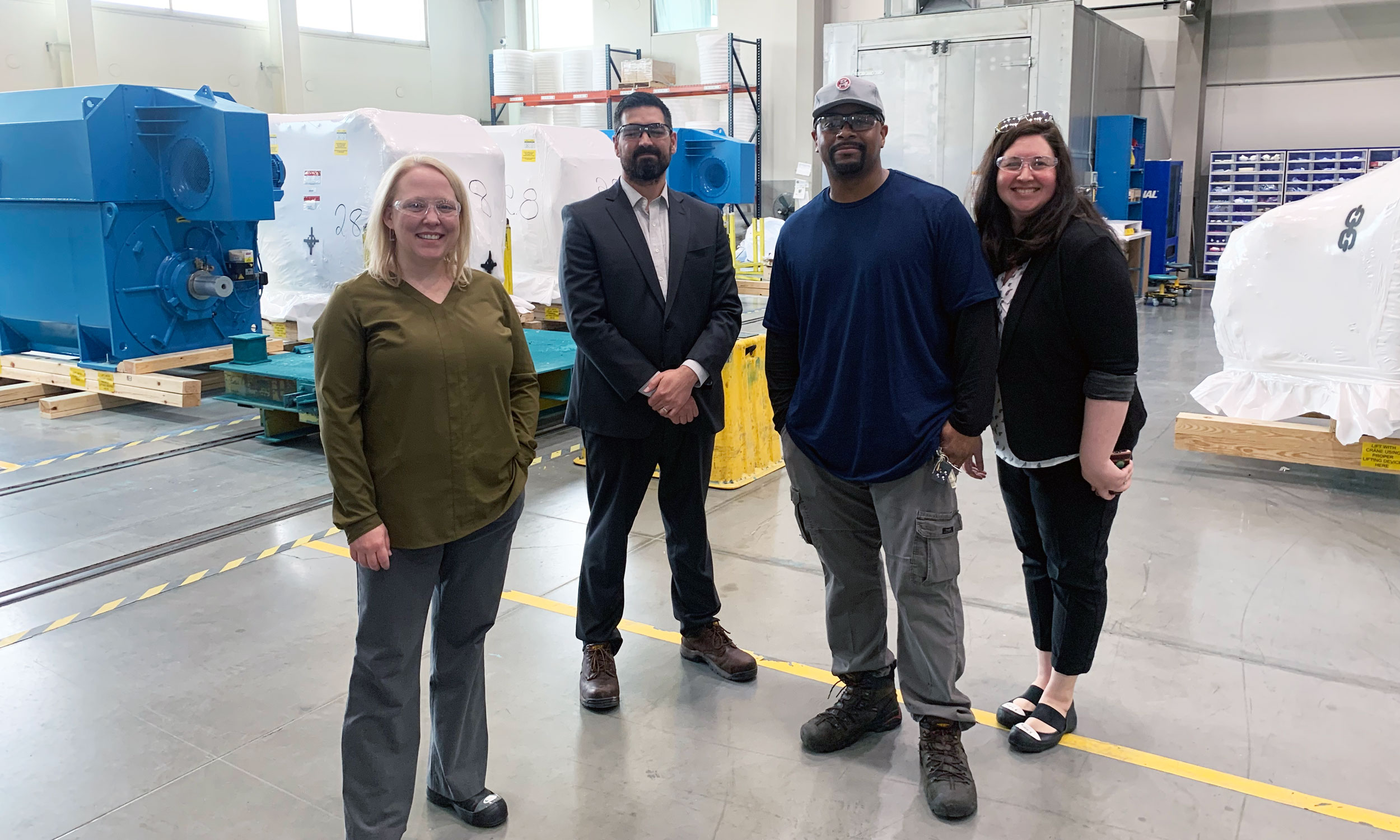
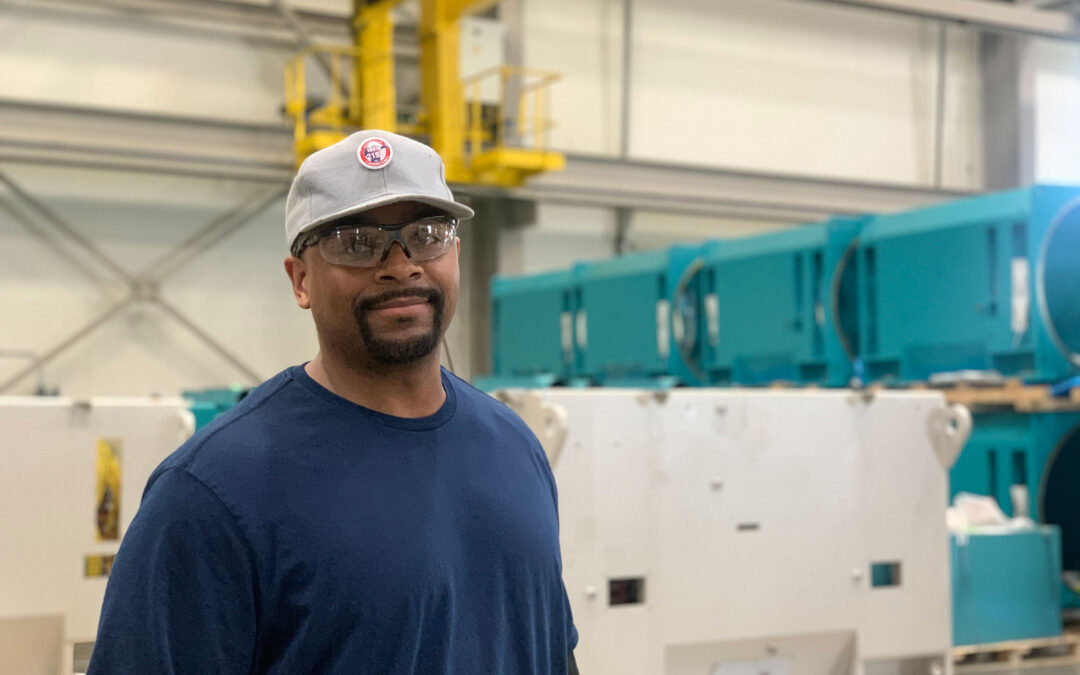
Akinlana Abdalla is tall and self-assured with a gentle, almost playful demeanor. He was “the kid who always got in trouble for taking his toys apart to see how they worked.” This curiosity and innate engineering mind make him particularly good at his job as a Wind Turbine Repair Specialist at Ingeteam in Milwaukee, WI, where teams of engineers and technicians specialize in supporting solar, wind, hydro, and other renewable energy products.
Akinlana was born in Milwaukee, where he now lives with his wife and children. He has an extensive background in commercial construction and is a Journeymen Carpenter by trade. His career took him from deep tunnel mining through Laborers’ Local 113 to building bridges for Zenith Tech, later starting a business with his wife, and eventually earning an undergraduate degree in general management. He was attracted to Ingeteam because he wanted to move away from management and get back to a more “hands-on” work environment aligned with his values.
Ingeteam is a global renewable energy solutions company. Their 140,000 square-foot state-of-the-art production facility in Milwaukee is the only place in the United States where wind turbines are built by an American workforce.
Ingeteam customers send wind turbine generators that cannot be repaired up the tower. Akinlana and his team perform mechanical and electrical diagnostics on the generators to determine their failure. Ingeteam then submits a report to the customer and a cost estimate for the needed repairs. If the customer decides to move forward with the repairs, Akinlana and his team “repair it and send it back to the customer like new,” adhering to the Code of Excellence established by IBEW 2150.


“You never know what you’re going to get,” Akinlana said. “There’s no monotony. Every day is something different. We could get the same [generator] models coming in on one truck, but all of them will have different issues. When we open it up, it’s just fun trying to get to the bottom of what the root cause of a failure is.”
While it seems as if Akinlana was born to do this work, he thinks his success is determined by having a positive attitude and complementing it with aptitude.
“If you have a good attitude, that’s 90% of it,” he said. “Developing your mechanical aptitude and other skills to complete a repair is something that can be taught. But it starts with just having a can-do attitude and just appreciating the opportunity to be able to do what you do.”
His passion for his work extends beyond his enjoyment of taking things apart and then putting them back together. Akinlana has a deep sense of the impact of his work.
“Ingeteam provides something imperative for preserving and conserving the future environment, not only for ourselves but for our children and generations to come,” he said. “Because we know that we have not learned to discipline ourselves from gluttonous consumption, we have to have green energy.”
“This job aligns with my personal social responsibility.” Akinlana continued. “It’s nice to work for an entity where you share a passion for ensuring that we preserve our environment. Being an avid outdoorsman, being out in nature with my children, fishing, and hiking, it’s important to me that I give back. To be able to work doing something that allows me to do that, I think is absolutely profound.”
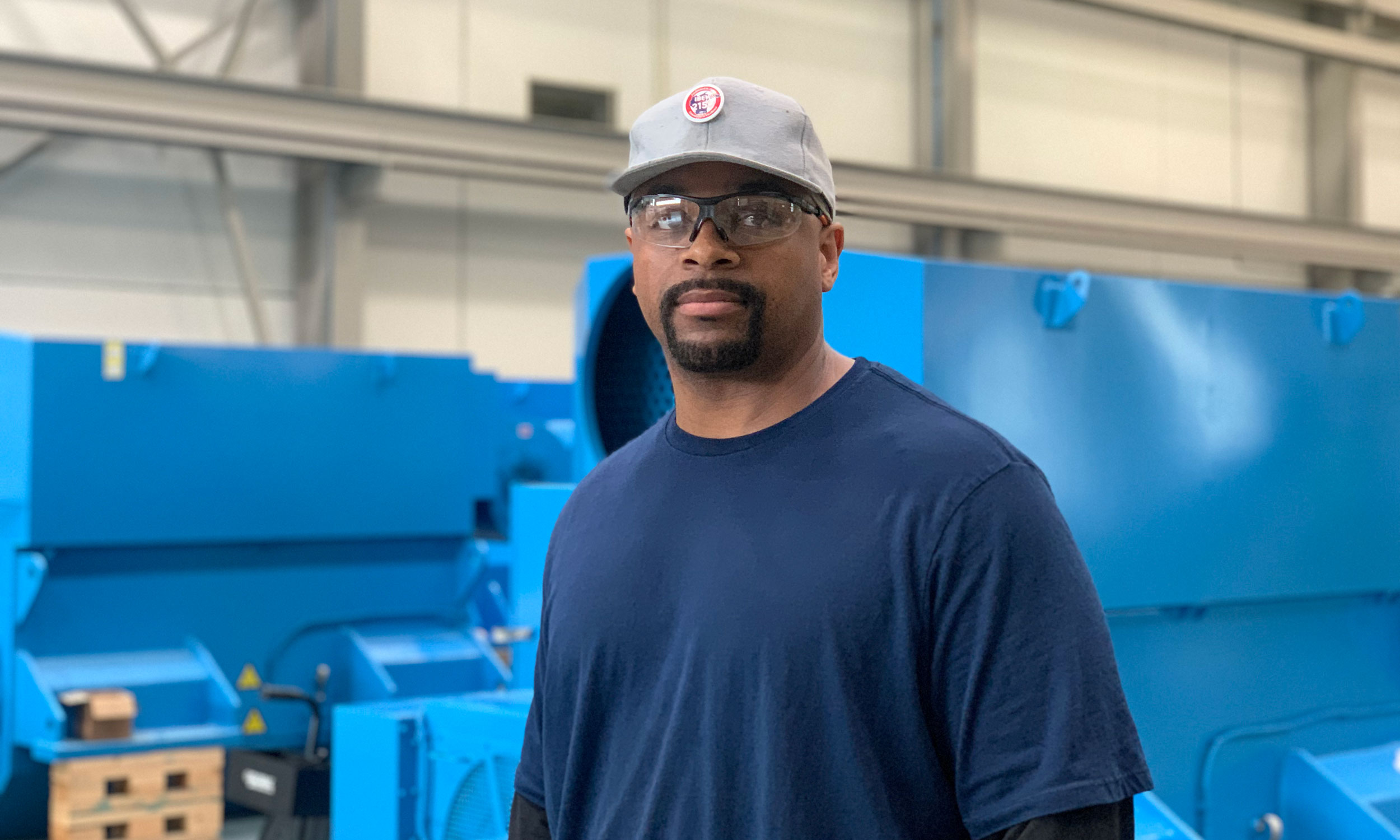

His team appreciates his passion and skills. Garan Chivinski is the Human Resources Manager at Ingeteam and the one who introduced him to RENEW Wisconsin.
“He’s a wealth of knowledge,” Garan said. “We’re seeing a time when those units [wind turbine generators] are coming back in, and they need to be serviced. They need some love and care to renew themselves and not create excess waste that they weren’t intended to create. AK [Akinlana] has really led that here for us, to get absolutely every single last spin, every single last value out of that resource possible for our customers and for the community. That’s why when you asked about somebody who might be your boots on the ground, somebody who’s the future of the wind industry in Wisconsin, this is the guy.”
Akinlana IS a wealth of knowledge. He’s also the kind of person who considers his work and actions and their effect on the world. This kind of thoughtfulness and passion is inspiring, and it’s easy to see why he is so respected and valued at Ingeteam.
“It’s nice to watch Elon Musk trying to fly off into another part of space,” Akinlana added. “But ultimately, when you see them go up in the rocket, you’re just going into another part of where you already are. Interesting, right? The reality is that we have this one small globe to live on, and no amount of money will get you away from that reality. Even if you set up something on Mars, you would have to come back here to get resources to live off of there. We have this [Earth], and we have to take care of this. Our level of consumption without trying to curb the adverse effects is damaging for the future. So that’s why this work is really, really important to me. I enjoy it every day. It’s not even work, not work at all.”